A.Classification
The genus Lycopodium is commonly known as club moss or Ground pine. It is a large genus comprising about 200 species, growing mainly in sub-tropical and tropical forests. Some species are distributed in Arctic and temperate regions also. All the species grow in moist and shady places, rich in organic compounds and humus.
B.Structure of the sporophye
1.,External Structure:- The sporophye , i.e., the plant body is well differentiated into stem, root and leaves.
Stem-. The stem is weak, slender and rhizomatous. In some species (L.clavatum and L.cernuum),etc, the stem or creeping on or the below the ground.
In others species the stem are erect and pendent. The branching of the stem is dichotomous. Stem and branches are covered with small leaves.
Roots- Roots arise from the underside of the creeping stem. They arise in clusters or singly. Branching of the root is dichotomous.
Leaves- Leaves are small, sessile, simple and lanceolate in shape with broad base. They arise spirally along the main axis of the stem. Mature leaves are provided with un-branched mid-vein.
2.Internal Structure:-
a) T.S of Stem:- The internal structure of aerial shoot show the following tissue systems-
Epidermis- Epidermis is one-celled in thickness and covered with cuticle. Stomata are present in the epidermal layer.
Cortex- Cortex is massive and divided into three zones-
a) outer zones composed of thick walled sclerenchymatous cells,
b) Middle zone composed of thin walled parenchymatous cells and
c) Innermost zone of one celled thickness known as endosermis.
Stele- Internal to the endosermis lie the pericylce composed of 3-6 layer of thin walled cells. The Stele is protostelic with exarch xylem.
The xylem core has radiating ribs forming a star like mass, or it may be in the form of isolated transverse strands, (actinostele and plectostele respectively). Phloem lies in space between the xylem Rays.
b) T.S of Root:- The root in transverse section shows-
Epidermis- Epidermis is single layered.
Cortex- Cortex is massive and composed of 2-zones
a) Outer zone with thick walled sclerenchyma cells and
b) Inner zone with thin walled parenchyma cells.
Stele- Stele is protostelic with monarch xylem vessels in young roots and diarch to deca-arch in older roots. The phloem cells lie in between the xylem Rays.
c) T.S of leaf :- The internal structure of leaf shows a single layered Epidermis covered with thick cuticle.
Beneath the Epidermis lies one type of meshophyll tissue, composed of rounded or angular parenchyma cells.
There is a single median, concentric vascular bundle.
c) Reproduction
Sporophyte of Lycopodium reproduces both by vegetative means and by production of spores-
1.Vegetative Reproduction- Vagetative Reproduction takes place by following methods-
a) By gameae or bulbils- These are modified Vagetative structure that arise as lateral outgrowth near the stem apex.
Each bulbil consists of short axis surrounded by a number of thick and fleshy leaves. The gameae fall on the ground and grow into a new plant.
b) Fragmentation- In this case, the branches gets separated from the parent plant due to the dead and decay of the older parts. The separated branches grow into new individuals plants.
c) By resting buds- In some species of Lycopodium , the tip of the rhizome or branch store food material and become thick with crowded leaves. These are resting buds. During unfavorable condition , the whole plant dies except the resting buds. It resume growth at the Advent of favourable condition , and produces a new individuals.
d) By root tubercles- Tubercles originated from the parenchymatous regions of the cortex. It consists of a group of cells with stored food material and protected by thick wall and have the capacity of germinates into a new plant individuals.
e) By adventious buds- Buds are developed from isolated bulbil leaves. It also develops in the stem near the Apex. Such buds can produce a new plant.
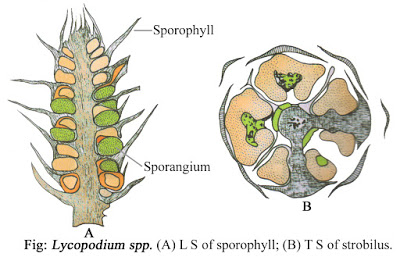
2. Spore Formation- In Lycopodium , the spores are formed in a specialized reproductive structure known as strobili or cone.
Each strobillus is a slender structure, sessile or stalked , simple , unbranched or dichoy branched , arising at the Apex of the stem or branches. It is a cylindrical structure measuring 2.5 cm and consist of central axis in which fertile leaves or sporophylls are spirally arranged. Each sporophyll bears a sporangium on the upper side at the basal portion.
Each sporangium is yellow or orange coloured and provided with sterile jacket layer of 2-3 layers of cells thick. Within the jackets layer is the fertile sporogenous tissue provided with nutritive tissue known as tapetum.
The sporogenous tissue later differentiates into spore mother cells, each of which by meiotic divisions produces spore tetrad.
Lycopodium is homosporous i.e., it is produced only one type of spores. As soon as the spores are developed haploid Gametophytic generation begins.
D. Structure of Gametophyte
Lycopodium is homosporous , hence the germination of spore produces homothallic gametophytic plant body or prothalli. Depending upon their nature, the prothalli of Lycopodium is of three types-
First type- In this type , the prothallus is very small , cylindrical ovoid in shape, short lived green in colour and develops on the surface of the ground. Such type of prothallus found in tropical species.
Second type- In this type, the prothallus is much larger (1-2 cm long) , more or less tuburous or carrot shaped , long lived , yellowish in colour or almost colourless and sub- terrenean. Such type of prothallus is found in creeping species.
Third type- This type of prothallus is intermediate between first and second types. This types of prothallus have irregularly shaped tuberous body (about 2mm in diameter) , colourless and sporophytic in nature.
Such type of prothallus is commonly found in epiphytic species.
Since the prothallus is homothallic, it bears both male and female sex organs, i.e., anthredia and archegonia in a single gametophytic plant body.
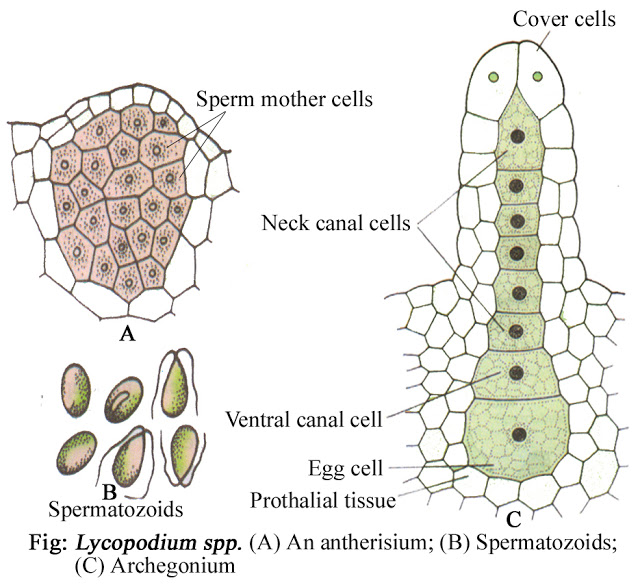
1.Antheredia:- Anthredia arise in several numbers in a gametophytic plant body.
They remain either wholly embedded in gametophytic tissue or projected slightly. They are generally oval in shape.
Each anthredium is surrounded by a jacket layer of one celled in thickness. Inside the jackets layer lies numerous sperm mother cells , which directly metamorphosed into small, cubical, biflagellate sperms.
2. Archegonium- Archegonium also arise in numbers in the gametophytic plant body. They also remain sunken with only their neck projecting outwardly. A mature archegonium consists of a neck , composed of a 6-13 neck canal cell, and a narrow venter, and composed of one ventral canal cell and egg cell.
3. Fertilization:- At maturity, the neck cell of the archegonium separate and the neck canal cell and ventral canal cell disorganize, leaving a passage for the entry of sperm.
The sperm after liberation from the anthredium make it's way through the neck and finally reached the egg.
On reaching the egg , one sperm fuses with the egg to complete the fertilization.
As a result of fertilization, a diploid zygote 2n is formed. With the formation of zygote , diploid sporophytic generation begins.
Divisions-Lycophyta
Class-Eligulopsdia
Order-Lycopodiales
Family-Lycopodiaceae
Genus-Lycopodium
The genus Lycopodium is commonly known as club moss or Ground pine. It is a large genus comprising about 200 species, growing mainly in sub-tropical and tropical forests. Some species are distributed in Arctic and temperate regions also. All the species grow in moist and shady places, rich in organic compounds and humus.
B.Structure of the sporophye
1.,External Structure:- The sporophye , i.e., the plant body is well differentiated into stem, root and leaves.
Stem-. The stem is weak, slender and rhizomatous. In some species (L.clavatum and L.cernuum),etc, the stem or creeping on or the below the ground.
In others species the stem are erect and pendent. The branching of the stem is dichotomous. Stem and branches are covered with small leaves.
Roots- Roots arise from the underside of the creeping stem. They arise in clusters or singly. Branching of the root is dichotomous.
Leaves- Leaves are small, sessile, simple and lanceolate in shape with broad base. They arise spirally along the main axis of the stem. Mature leaves are provided with un-branched mid-vein.
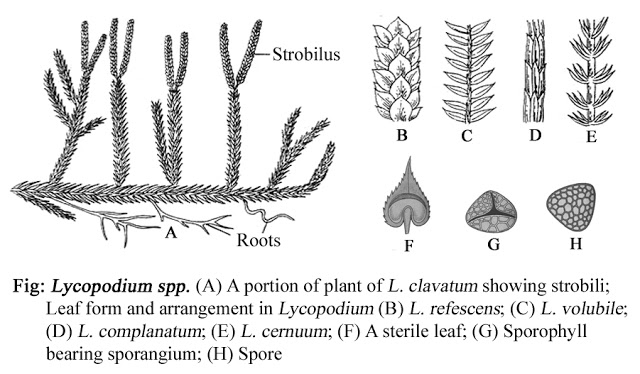 |
| Source wikipedia |
2.Internal Structure:-
a) T.S of Stem:- The internal structure of aerial shoot show the following tissue systems-
Epidermis- Epidermis is one-celled in thickness and covered with cuticle. Stomata are present in the epidermal layer.
Cortex- Cortex is massive and divided into three zones-
a) outer zones composed of thick walled sclerenchymatous cells,
b) Middle zone composed of thin walled parenchymatous cells and
c) Innermost zone of one celled thickness known as endosermis.
Stele- Internal to the endosermis lie the pericylce composed of 3-6 layer of thin walled cells. The Stele is protostelic with exarch xylem.
The xylem core has radiating ribs forming a star like mass, or it may be in the form of isolated transverse strands, (actinostele and plectostele respectively). Phloem lies in space between the xylem Rays.
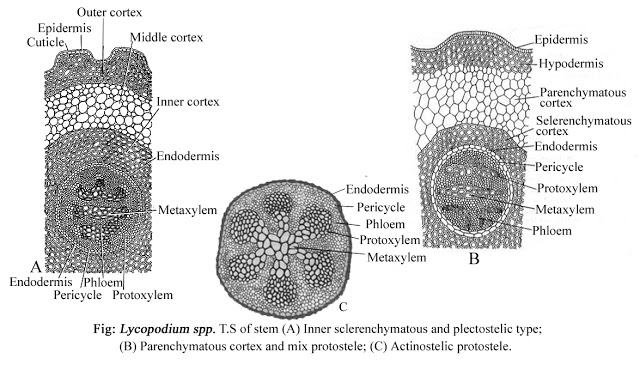 |
| Source Wikipedia |
b) T.S of Root:- The root in transverse section shows-
Epidermis- Epidermis is single layered.
Cortex- Cortex is massive and composed of 2-zones
a) Outer zone with thick walled sclerenchyma cells and
b) Inner zone with thin walled parenchyma cells.
Stele- Stele is protostelic with monarch xylem vessels in young roots and diarch to deca-arch in older roots. The phloem cells lie in between the xylem Rays.
c) T.S of leaf :- The internal structure of leaf shows a single layered Epidermis covered with thick cuticle.
Beneath the Epidermis lies one type of meshophyll tissue, composed of rounded or angular parenchyma cells.
There is a single median, concentric vascular bundle.
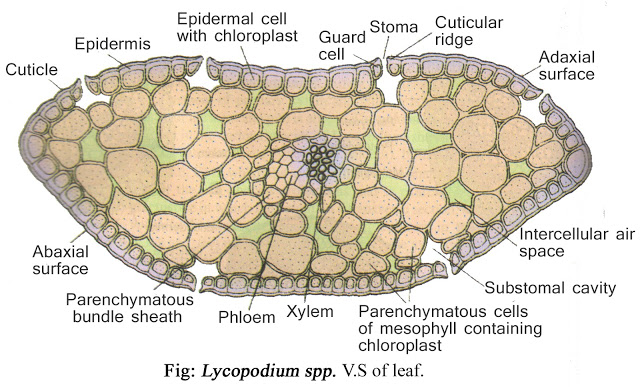 |
| Source wikipedia |
c) Reproduction
Sporophyte of Lycopodium reproduces both by vegetative means and by production of spores-
1.Vegetative Reproduction- Vagetative Reproduction takes place by following methods-
a) By gameae or bulbils- These are modified Vagetative structure that arise as lateral outgrowth near the stem apex.
Each bulbil consists of short axis surrounded by a number of thick and fleshy leaves. The gameae fall on the ground and grow into a new plant.
b) Fragmentation- In this case, the branches gets separated from the parent plant due to the dead and decay of the older parts. The separated branches grow into new individuals plants.
c) By resting buds- In some species of Lycopodium , the tip of the rhizome or branch store food material and become thick with crowded leaves. These are resting buds. During unfavorable condition , the whole plant dies except the resting buds. It resume growth at the Advent of favourable condition , and produces a new individuals.
d) By root tubercles- Tubercles originated from the parenchymatous regions of the cortex. It consists of a group of cells with stored food material and protected by thick wall and have the capacity of germinates into a new plant individuals.
e) By adventious buds- Buds are developed from isolated bulbil leaves. It also develops in the stem near the Apex. Such buds can produce a new plant.
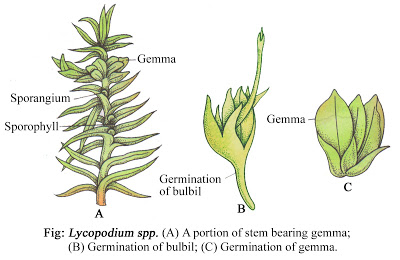 |
| Source Wikipedia |
Each strobillus is a slender structure, sessile or stalked , simple , unbranched or dichoy branched , arising at the Apex of the stem or branches. It is a cylindrical structure measuring 2.5 cm and consist of central axis in which fertile leaves or sporophylls are spirally arranged. Each sporophyll bears a sporangium on the upper side at the basal portion.
Each sporangium is yellow or orange coloured and provided with sterile jacket layer of 2-3 layers of cells thick. Within the jackets layer is the fertile sporogenous tissue provided with nutritive tissue known as tapetum.
The sporogenous tissue later differentiates into spore mother cells, each of which by meiotic divisions produces spore tetrad.
Lycopodium is homosporous i.e., it is produced only one type of spores. As soon as the spores are developed haploid Gametophytic generation begins.
 |
| Source Wikipedia |
D. Structure of Gametophyte
Lycopodium is homosporous , hence the germination of spore produces homothallic gametophytic plant body or prothalli. Depending upon their nature, the prothalli of Lycopodium is of three types-
First type- In this type , the prothallus is very small , cylindrical ovoid in shape, short lived green in colour and develops on the surface of the ground. Such type of prothallus found in tropical species.
Second type- In this type, the prothallus is much larger (1-2 cm long) , more or less tuburous or carrot shaped , long lived , yellowish in colour or almost colourless and sub- terrenean. Such type of prothallus is found in creeping species.
Third type- This type of prothallus is intermediate between first and second types. This types of prothallus have irregularly shaped tuberous body (about 2mm in diameter) , colourless and sporophytic in nature.
Such type of prothallus is commonly found in epiphytic species.
Since the prothallus is homothallic, it bears both male and female sex organs, i.e., anthredia and archegonia in a single gametophytic plant body.
 |
| Source Wikipedia |
1.Antheredia:- Anthredia arise in several numbers in a gametophytic plant body.
They remain either wholly embedded in gametophytic tissue or projected slightly. They are generally oval in shape.
Each anthredium is surrounded by a jacket layer of one celled in thickness. Inside the jackets layer lies numerous sperm mother cells , which directly metamorphosed into small, cubical, biflagellate sperms.
2. Archegonium- Archegonium also arise in numbers in the gametophytic plant body. They also remain sunken with only their neck projecting outwardly. A mature archegonium consists of a neck , composed of a 6-13 neck canal cell, and a narrow venter, and composed of one ventral canal cell and egg cell.
 |
| Source Wikipedia |
The sperm after liberation from the anthredium make it's way through the neck and finally reached the egg.
On reaching the egg , one sperm fuses with the egg to complete the fertilization.
As a result of fertilization, a diploid zygote 2n is formed. With the formation of zygote , diploid sporophytic generation begins.
















0 Comments
If you have any query let me know.