Ovule Meaning
The ovule is a component of the makeup of the feminine sex organ in seed plants. It’s the place where female reproductive cells are made and contained, and it's what eventually develops into a seed after fertilization, just for the seed to then ripen and produce a complete adult plant. Ovules are contained in ovaries at rock bottom of a vase-like structure, the carpel, which features a neck called a method and a gap at the highest , called a stigma. Ovule starts swell After fertilization and it's wall also starts to toughen in preparation to become a seed, while the ovary starts to grow around it and becomes the fruit. Keep in mind that some plants, just like the avocado, have one ovule in their ovary, while others, just like the kiwifruit, have many, which become many seeds within the fruit. Another way that plants differ with regards to their ovules is that the place where the ovules are found. Specifically, the ovules are found inside of the ovary within the carpel.
Parts of Ovules
The ovule is made of Nucellus, the part of the ovules that form the outermost layer, and the female gametoohyte ( called embryosac in flowering plants), which are found at the distinct center.
The Nucellus
The nucellus is that the largest a part of the ovule. It houses the embryo sac also as nutritive tissue and truly remains present in some flowering plants after fertilization as a source of nutrients for the embyo.
The Integuments
The integument is that the tough outer protective layer of the ovule. In the diagrams below we will see that gymnosperms, like pine trees and spruce trees, usually have one integument in an ovule, so we call them unitegmic. On the opposite hand, angiosperms, like maples and daisies, typically have two integuments, and that we call them bitegmic. The integument encloses the nucellus apart from alittle gap, which is named the micropyle.
Ovule diagram
The Female Gametophyte
This is the part of the ovules that contains the gamete-producing sex organs, which are critical for sexual reproduction. Single set of unpaired chromosomes, contains by the female gametoohyte, this is haploid in nature. It is commonly called megagametoohyte or embryo sac.
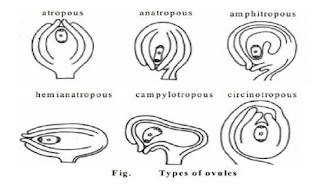
Types of Ovules
Ovules are separated into six categories supported their shapes:
Orthotropous (Atropous)
This is where the body of those ovules is straight in order that the chalaza, where the nucellus and integuments merge, the funicle, which attaches the ovule to the placenta, and the micropyle are all aligned.
Anatropous
In this case, the ovules become completely inverted during development in order that the micropyle lies on the brink of the hilum. The hilum may be a scar that marks the purpose where the seed was attached to the fruit wall by the funicle.
Hemi Anatropous
The body of those ovules becomes at a right angle in reference to the funicle, so it's just like the ovule is lying on its side.
Campylotropous
The body of this sort is bent and therefore the alignment between the chalaza and micropyle is lost. The embryo sac is only slightly curved.
Amphitropous
The body of the ovule is extremely much curved that the embryo sac and therefore the ovule itself take the form of a horseshoe.
Circinotropous
The funicle during this case is particularly long that it creates an almost full revolve around the ovule whose micropyle is ultimately pointing upwards.
Ovules function
The ovule plays a vital role in sexual reproduction. Once a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower of its same species, it sends out a plant part down through the design . This tube then enters in the ovary and reaches the ovule of the plant. Once that happens , fertilization can arise because the nucleus of the pollen grain is shipped down the tube to merge with the nucleus within the embryo sac.
Related Terms
Anther – Anther is the part of the stamen that contains male Gametophyte or pollen grains.
Asexual Reproduction – In asexual reproduction the genetically identical offspring are produced without the formation of gametes from a single parent.
Diploid – A organism or nuceleus, cell that contains two set of chromosomes, one from male parent and another from female parent.
Pollination– The transfer of pollen to the female reproductive organs of the same plant or a different plant of the same species.















0 Comments
If you have any query let me know.