ENTOMOGENOUS FUNGI
Entomogenous means growing on or in the bodies of insects' and strictly speaking applies to all those organisms including bacteria and fungi. However, the word is most often used to describe filamentous fungi that invade their insects hosts by penetrating directly through the cuticle.
Many common and Important entomogenous fungi belong to the order hypocreales of the ascomycota - Isaria, Hirsutella, Cordyceps, and of the order Entomophtorales of the zygomycota - Entomophthora, Zoophthora , Pandora etc.
LIFE CYCLE-
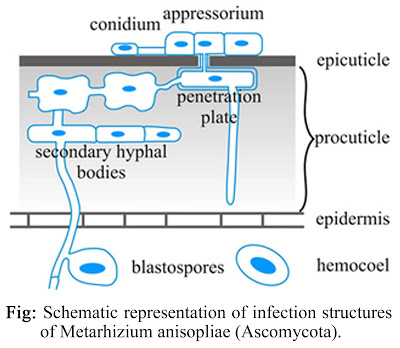
These fungi usually attach to the external body surface of insects in the form of microscopic spores (usually asexual, mitosporic spores also called conidia). Under the right condition of temperature and ( usually high ) humidity, these spores germinates , grow as hyphae and colonize the insects cuticle , which they bore through by way of enzymatic hrdrolysis reaching the insects body cavity.
Then, the fungal cells proliferate in the host body cavity, usually as walled hyphae or in the form of walless protoplast (depending on the fungus involved). After the some time insects is usually killed (sometime by fungal toxins) and new propagules (spore) are formed in or on the insect if environmental condition are again favourable. High humidity is usually required for sporulation.
Then, the fungal cells proliferate in the host body cavity, usually as walled hyphae or in the form of walless protoplast (depending on the fungus involved). After the some time insects is usually killed (sometime by fungal toxins) and new propagules (spore) are formed in or on the insect if environmental condition are again favourable. High humidity is usually required for sporulation.
 |
| Source Wikipedia |
IMPORTANCE
Since they are considered natural mortality agents and environmentally safe, there is worldwide interest in the use and manipulation of entomopathogenic fungi for biological control of insects and other arthropod pests. In particular the asexual phases of ascomycota (Isaria, Metarhizium, Hirsutella etc) are under intense scrutiny due to the traits favouring their use as biological insecticides.
The Entomophthorales are often reported as causing high levels of martality in nature. These fungi are highly virulent. The anamorphic Ascomycota (Metarhizium, Beauveria, etc) are reported as causing epizootics less frequently in nature.











0 Comments
If you have any query let me know.