What is Nodal Anatomy?
Nodal anatomy is the branch of botany which deals with internal structure and organization of plant or the plant organs are called plant anatomy.
N.Grew (1641-1712) is known as father of plant anatomy.
K.A Chaudhary is the father of indian plant anatomy.
Anatomy of Nodal and internodal region are different:-
The stem of plant is differentiated into nodes and internodes. The anatomical features of internodal region are is quiet different from that of the internodal region. This anatomical difference is due to the prescence of vascular supply to the leaves and branches from the main vascular cylinder of the stem.
Nodal region of higher plants posses leaf gaps & leaf traces:-
Each leaf that originates from the node, of higher plants possess vascular tissue of the leaves are connected to that of the stem. A vascular strand that extends between the vascular cylinder of stem and the leaf is called leaf trace or foliar trace.
Even if the trace possess both xylem and phloem the relative ammount of xylem will be more in the leaf trace than phloem. More over the proximal portion contain only the xylem. Whereas, the distil end of the leaf trace contain both xylem and phloem. Leaf trace help to transport water and minerals from the xylem to the leaf lamina for photosynthesis. The circulation of photosynthetic products from the leaf lamina to the phloem of the stem is also facilated by phloem strands in the leaf traces.
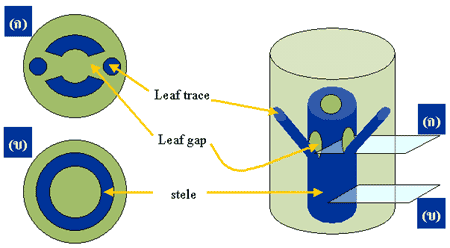 |
| Nodal anatomy of higher plants |
Nodes are classified on the basis of number of leaf gap and leaf traces:-
The number and nature of leaf trace and leaf gaps varies in different plants. There are three main nodes are described in angiosperms.
1) Unilacunar
2) Trilacunar
3) Multilacunar
1) Unilacunar:-
A unilacunar nodes possess only a single leaf gap to a leaf. Each leaf may possess one or two or three leafs traces.
Ex:- Nerium, Chenopodium album
 |
| Unilacunar nodes posses single leaf gap |
2) Trilacunar:-
A trilacunar node possess three leaf gapes and three leaf traces. Among these three leaf traces, the middle one will be larger and other two laterals will be smaller.
Ex:- Azadirachta indica
 |
| Trilacunar nodes posses three leaf gap and three leaf traces |
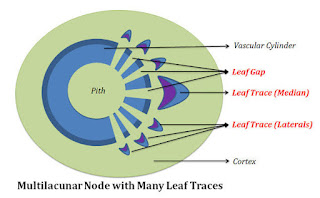
3) Multilacunar:-
A multilacunar node possess many leaf traces and many leaf gaps. Among these 3 leaf traces the middle one is larger than other two lateral leaf traces.
Ex:- Coriandrum sativum
Nodal anatomy shows the phylogenetic primitiveness or advancements:-
A unilacunar nodes with two traces is considered to be the most primitive type of node among angiosperms.
Significance, the nodal anatomy is the good taxonomic character used in the systematics of higher plants.
Key questions
- What is nodal anatomy?
- What is leaf trace and leaf gap?
- What is the region of a stem between two nodes?
- What is leaf trace in plants?
- Nodal anatomy relation to taxonomy?
- Role of nodal anatomy in taxonomy?
- Nodal evolution?
- Anatomy of node?
- Trilacunar node example?
- Branch trace and branch Gap?
- Leaf trace?
- Nodal anatomy of equisetum?











0 Comments
If you have any query let me know.